- Oncogenes: mutated proto-oncogenes that drive proliferation (e.g., Ras).
- Tumor Suppressors: genes that inhibit division (e.g., p53, RB); loss leads to unrestrained growth.
- Apoptosis Evasion: cancer cells disable programmed cell death pathways.
Chapter Summary
Cancer arises when normal regulatory mechanisms that control cell division fail. Genetic mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressors, along with environmental factors, drive uncontrolled proliferation. Clinical strategies include detection, staging, treatment, and prevention.
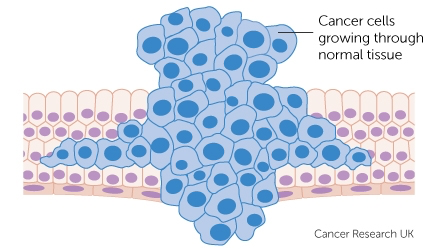
What Is Cancer?
Cancer is a collection of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth that can invade surrounding tissues and spread (metastasize) to distant organs.
Key Molecular Pathways
Key Terms
- Metastasis: spread of cancer cells beyond original site
- Angiogenesis: new blood vessel formation feeding tumors
- Carcinogen: agent that induces cancer (e.g., UV, tobacco)
Quiz Yourself
1. Which gene type inhibits cell division and prevents tumor formation?
2. Which of the following is a characteristic of cancer?