- RNA Polymerase II: synthesizes pre-mRNA in eukaryotes.
- 5′ Capping: protects mRNA and aids ribosome binding.
- Ribosome: decodes mRNA codons into amino acids.
Chapter Summary
Protein synthesis involves: (1) transcription of DNA into pre-mRNA, (2) processing of pre-mRNA (capping, polyadenylation, splicing), and (3) translation of mature mRNA into polypeptides. Multiple RNA types and enzymes ensure high fidelity and regulation.
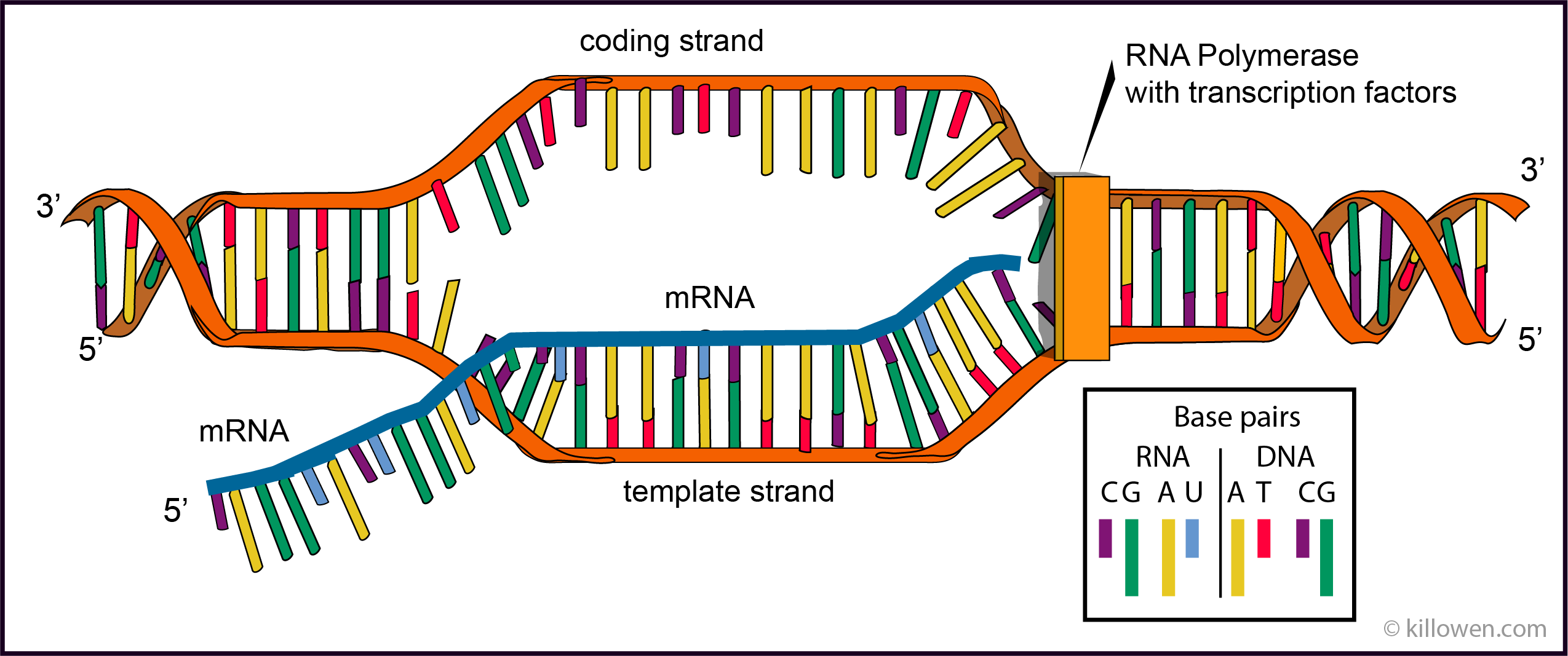
Transcription
RNA polymerase binds promoter, separates DNA strands, synthesizes pre-mRNA 5′→3′ using the template strand.
Key Enzymes & Mechanisms
Regulation & Clinical Correlations
- Alternative Splicing: one gene → multiple proteins; mutations can cause disease (e.g., β-thalassemia).
- Ribosomal Inhibitors: antibiotics like tetracycline block translation in bacteria.
Key Terms
- Codon: three-base mRNA sequence specifying an amino acid.
- Anticodon: three-base tRNA sequence complementary to codon.
- Start/Stop Codons: AUG initiates, UAA/UAG/UGA terminate translation.
Quiz Yourself
1. Which enzyme synthesizes pre-mRNA?
2. What modification protects mRNA from degradation?
3. In which organelle does translation occur?