Caused by a point mutation in β-globin gene: Glu→Val at position 6. Heterozygotes (HbA/HbS) have some protection against malaria (“balanced polymorphism”).
Chapter Summary
Learn Mendelian inheritance from mono- to trihybrid crosses, Punnett squares, pedigrees, sex-linked traits, dominance patterns, Hardy–Weinberg, and speciation.
Interactive Di-hybrid Cross (AaBb × AaBb)
Drag the four gametes from each parent into the slots below:
Parent 1 Gametes:
AB
Ab
aB
ab
Parent 2 Gametes:
AB
Ab
aB
ab
Drop Parent 1 gametes here →
Drop Parent 2 gametes here ↓
Sickle Cell Anemia
Trihybrid Crosses & Probability
Three genes assort independently. Probability of a specific genotype = product of individual probabilities (e.g. 3/4 × 3/4 × 3/4 = 27/64 for all dominant traits).
Pedigree Analysis
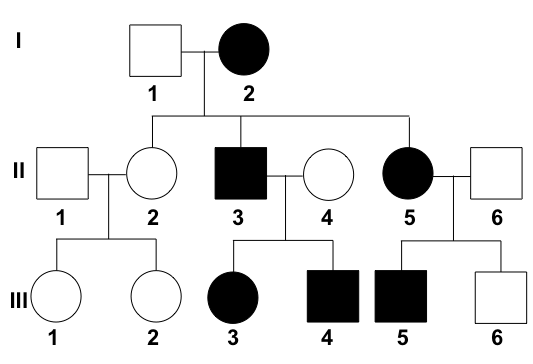
Use symbols to track inheritance patterns across generations.
Sex-Linked Traits & Dominance
- Complete Dominance: one allele masks another (e.g. Pp).
- Partial Dominance: heterozygote shows intermediate phenotype (e.g. red/white snapdragon → pink).
- X-Linked Recessive: more common in males (e.g. color blindness, hemophilia).
Key Terms
- Allele, genotype, phenotype
- Monohybrid, dihybrid, trihybrid crosses
- Punnett square, probability
- Pedigree symbols and analysis
- Dominance patterns, sex-linked inheritance
Quiz Yourself
1. In a dihybrid cross AaBb × AaBb, what % of offspring are A_B_?